The Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCO)
PCO is the most common hormonal disorder in women. The syndrome does not manifest itself in equal strength and with same symptoms in all cases.
|
What are the symptoms of PCO?
Elevated levels of male sex hormones (e.g. testosterone) lead to:
- Acne
- Hair loss
- Thin hairs
- Widow's peak resp. high male hairline at the forehead
- Head skin visible under the hairs
- Facial hair around the upper lip and the cheeks
- Noticeable hairs of the inner thighs and the lower abdomen
- Weight problems, overweight, ravenous appetite attacks
- Problems with the monthly cycle: usually an irregular menstruation occurs after 2-3 months
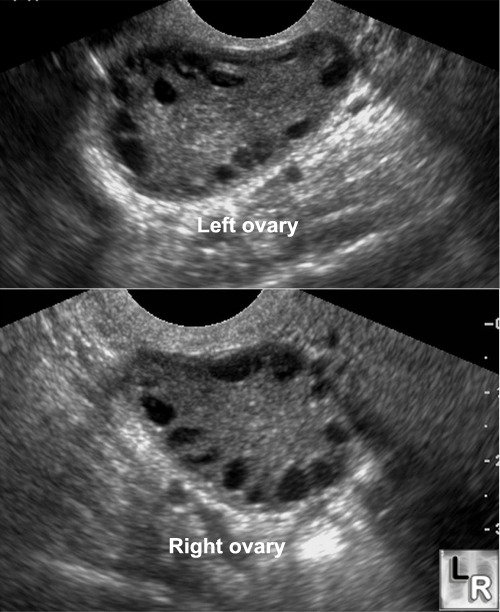
- The ultrasonic picture of the ovaries is conspicuous: they are enlarged and numerous small follicles, resp. "cysts" are found "like beads on a string" on the surface. Hence the description poly (=many) cystic (=sacs) ovaries
- Inability to conceive
- Striking hormone levels: during the menstruation, the LH (luteinizing hormone) is pronouncedly higher than the FSH (follicle stimulating hormone), e.g. LH 12.5 units and FSH 5.2 units.
Go to treatment of PCO
|
 |



